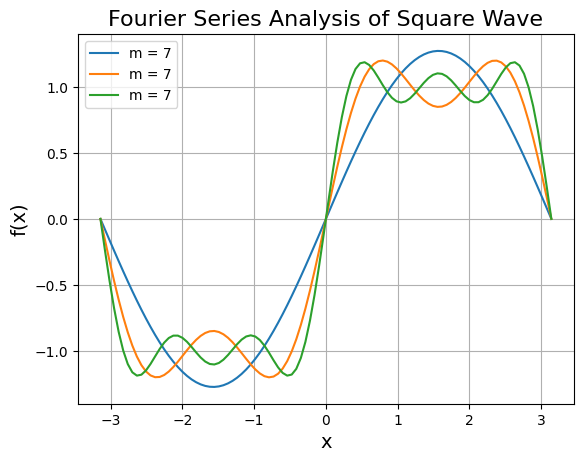
Fourier Series Analysis - Square Wave
Fourier series for a square wave function:
Algorithm: Fourier Series for a Square Wave
This algorithm visualizes the Fourier series approximation of a square wave function using Python.
Step 1: Import Libraries
Import
numpyfor numerical operations.Import
matplotlib.pyplotfor plotting.
Step 2: Initialize Constants
Set amplitude constant
k = 1.Use
np.pito represent π.
Step 3: Loop Over Odd Harmonic Counts
Loop through odd values of
mfrom 3 to 7 (inclusive) with a step of 2.These represent the number of Fourier terms used in each approximation.
Step 4: Generate Values
For each
m:Create 100 evenly spaced
xvalues from-πtoπ.Generate array
ncontaining odd numbers from 1 up tom(exclusive), reshaped for broadcasting.
Step 5: Compute Fourier Series Sum
Use the formula:
\[f(x) = \frac{4k}{\pi} \sum_{n=1,3,5,\ldots}^{m} \frac{1}{n} \sin(nx)\]Perform the calculation using broadcasting:
Multiply
xvalues with eachn.Apply
sin(), divide byn, and sum across all terms.Multiply the result by
(4k/π).
Step 6: Plot the Result
Plot the calculated Fourier series for each
m.Label each line with its corresponding
m.
Step 7: Format the Plot
Add axis labels:
xandf(x).Add a title: “Fourier Series Analysis of Square Wave”.
Show a legend for clarity.
Add grid lines for better visualization.
Step 8: Display the Plot
Use
plt.show()to render the plot.
Output:
Multiple curves showing how the square wave approximation improves as more Fourier terms are added.
[1]:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
[2]:
k = 1
pi = np.pi
for m in range(3, 9, 2):
xrange = np.linspace(-pi, pi, 100);xrange
n = np.arange(1, m, 2)[:, np.newaxis];n
fsum = (4*k/pi)*np.sum(np.sin(xrange*n)/n, axis=0)
plt.plot(xrange, fsum, label = f"m = {m}")
plt.xlabel("x", fontsize =14)
plt.ylabel("f(x)", fontsize =14)
plt.title("Fourier Series Analysis of Square Wave", fontsize = 16)
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()
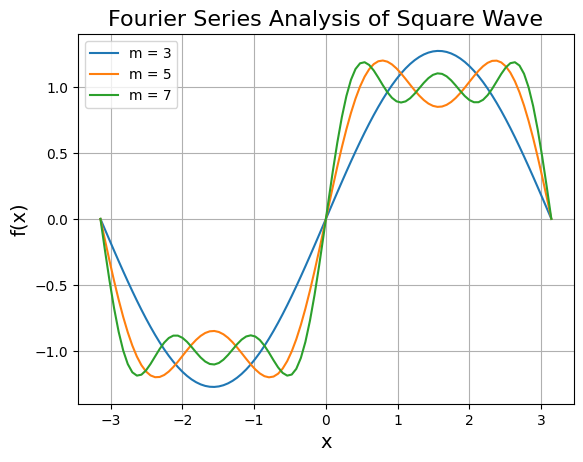
[3]:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
k = 1
pi = np.pi
xrange = np.linspace(-pi, pi, 100)
# Create an array for m values (3, 5, 7)
m_values = np.arange(3, 9, 2)[:, np.newaxis] # Shape (3,1) for broadcasting
# Create an array for n values for each m
n_values = [np.arange(1, m, 2)[:, np.newaxis] for m in m_values.flatten()]
# Compute fsum for all m_values at once
fsum_list = [(4 * k / pi) * np.sum(np.sin(xrange * n) / n, axis=0) for n in n_values]
# Plot all the curves at once
for fsum in fsum_list:
plt.plot(xrange, fsum, label = f"m = {m}")
plt.xlabel("x", fontsize =14)
plt.ylabel("f(x)", fontsize =14)
plt.title("Fourier Series Analysis of Square Wave", fontsize = 16)
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()