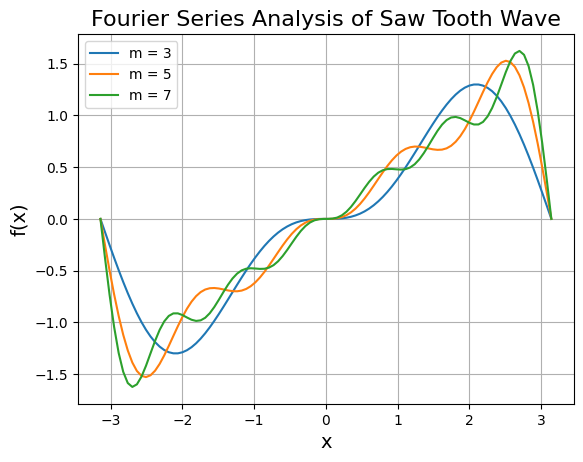
Fourier Series Analysis - Saw Tooth Wave
A sawtooth wave is a periodic function that increases linearly and then drops sharply. It can be expressed using a Fourier series as: \begin{equation} f(x) = \sum_{n=1}^{\infty}\frac{(-1)^{(n+1)}}{n}\sin nx \end{equation}
Algorithm: Fourier Series for a Sawtooth Wave
This algorithm computes and visualizes the Fourier series approximation of a sawtooth wave, which increases linearly and drops sharply at the end of each period.
Step 1: Import Required Libraries
Import
numpyfor array and mathematical operations.Import
matplotlib.pyplotfor plotting the wave.
Step 2: Define Constants
Define
pias the mathematical constant π using NumPy.
Step 3: Loop Through Harmonic Terms
Loop through odd values of
mfrom3to7(exclusive upper bound9, step2).This determines the number of Fourier terms (harmonics) used in the approximation.
Step 4: Generate x and n Values
xrange: 100 values linearly spaced between-πandπ.n: Array of integers from1tom-1, reshaped as a column vector for broadcasting.
Step 5: Compute Fourier Series Sum
Apply the formula:
\[f(x) = \sum_{n=1}^{m} \frac{(-1)^{n+1}}{n} \sin(nx)\]Use NumPy to compute the sum:
Calculate
((-1)^(n+1)) * sin(n * x) / nand sum across harmonics.Store the result in
fsum.
Step 6: Plot the Result
Plot
fsumagainstxrangefor each value ofm.Label each curve accordingly.
Step 7: Customize Plot
Set labels for the x and y axes.
Add a title: “Fourier Series Analysis of Saw Tooth Wave”
Add a legend and grid for visual clarity.
Step 8: Display the Plot
Use
plt.show()to render the final visualization.
Output:
Multiple curves representing the sawtooth wave using increasing numbers of harmonics (Fourier terms).
[1]:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
[2]:
pi = np.pi
for m in range(3, 9, 2):
xrange = np.linspace(-pi, pi, 100);xrange
n = np.arange(1, m)[:, np.newaxis]
fsum = np.sum(((-1)**(n+1)) * np.sin(n * xrange) / n, axis=0)
plt.plot(xrange, fsum, label = f"m = {m}")
plt.xlabel("x", fontsize =14)
plt.ylabel("f(x)", fontsize =14)
plt.title("Fourier Series Analysis of Saw Tooth Wave", fontsize = 16)
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()